Approximate Bayesian Inference for Robust Speech Processing
The performance of speech processing applications such as speech and speaker recognition is adversely affected by the presence of noise in all acoustic environments. In order for robust performance in a wide variety of noisy environments, it is important to have an adequate means of enhancing the noisy speech. Speech enhancement is an important inference problem due to the numerous potential applications in communication, human machine interaction, and medicine. It is therefore interesting to explore the application of Bayesian methods to this inference problem due to the superior performance of Bayesian methods in other domains. However, the major limitation of Bayesian methods is their computational complexity. In our work, we apply recently developed approximate Bayesian inference techniques to the problem of robust speech processing. Approximate Bayesian inference techniques such as variational Bayesian inference and expectation propagation achieve performance similar to full Bayesian inference at lower computational cost.
Our work so far has concentrated on the area of joint speech enhancement and speaker identification. Here the prior distribution of the speech is speaker dependent and this allows us to infer both identity and the clean speech jointly from noisy observations. A variational Bayesian algorithm has been derived that exchanges information between the speech enhancement task and the speaker identification task. It is based on the intuition that with cleaner speech, identification decisions are more accurate and with a better identification decision, a speaker specific prior will lead to better enhancement performance. This interplay between speech enhancement and identification is captured in the iterative variational Bayesian algorithm and is illustrated below.
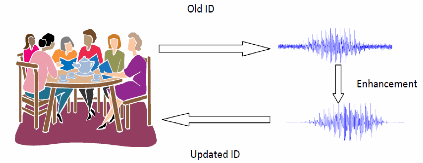
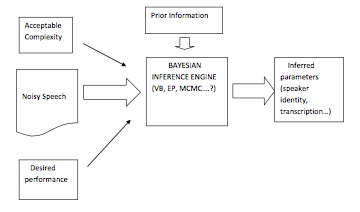
A further goal of this research is to determine the tradeoff between performance and computational complexity over the spectrum of approximate Bayesian inference techniques when applied to this problem of robust speech processing. In particular, our work has developed robust speech processing algorithms utilizing variational Bayesian inference, expectation propagation, and Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling approximate inference techniques, and the goal is to apply these to a series of robust speech processing problems and compare their performance and complexity. This would allow us to determine what inference technique to employ for a particular speech processing problem. This is illustrated in the figure below.
Funding for this Topic:
 Supported in part by the National Science Foundation under the CAREER award CCF-1053702
and the award IIS-1152288.
Supported in part by the National Science Foundation under the CAREER award CCF-1053702
and the award IIS-1152288.
Relevant Publications & Presentations
[1] Ciira wa Maina, “Approximate Bayesian Inference for Robust Speech Processing,” Ph.D. dissertation, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://www.ece.drexel.edu/walsh/Maina_PhD.pdf
[2] C. Maina and J. M. Walsh, “Log Spectra Enhancement using Speaker Dependent Priors for Speaker Verification,” IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech, Language Processing., submitted March 14, 2011. Revised July 15, 2011.
[3] Ciira wa Maina and John MacLaren Walsh, “Log Spectra Enhancement using Speaker Dependent Priors for Speaker Verification,” in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2011), May 2011. [Online]. Available: http://www.ece.drexel.edu/walsh/Maina_ICASSP_05_11.pdf
[4] ——, “Compensating for Noise and Mismatch in Speaker Verification Systems Using Approximate Bayesian Inference,” in 45th Conference on Information Sciences and Systems CISS 2011, Mar. 2011. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/CISS.2011.5766174
[5] C. Maina and J. M. Walsh, “Joint Speech Enhancement and Speaker Identification Using Approximate Bayesian Inference,” IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech, Language Processing., vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 1517–1529, Aug. 2011. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2010.2092767
[6] Ciira wa Maina and John MacLaren Walsh, “Joint Speech Enhancement and Speaker Identification Using Approximate Bayesian Inference,” in 44th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, Mar. 2010. [Online]. Available: http://www.ece.drexel.edu/walsh/Maina_CISS_10.pdf
[7] ——, “Robust Speaker Recognition Using Approximate Bayesian Inference,” Dec. 2009, Demonstration at Neural Information Processing Symposium (NIPS) 2009.
[8] ——, “Joint Speech Enhancement and Speaker Identification Using Monte Carlo Methods,” in Interspeech 2009, Sep. 2009. [Online]. Available: http://www.ece.drexel.edu/walsh/Maina_Interspeech_09.pdf
[9] Y. E. Kim, J. M. Walsh, and T. M. Doll, “Comparison of a Joint Iterative Method for Multiple Speaker Identification with Sequential Blind Source Separation and Speaker Identification,” in Odyssey 2008: The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop, Jan. 2008. [Online]. Available: http://www.ece.drexel.edu/walsh/Odyssey2008.pdf
[10] J. M. Walsh, Y. E. Kim, and T. M. Doll, “Joint iterative multi-speaker identification and source separation using expectation propagation,” in IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, Oct. 2007, pp. 283 – 286. [Online]. Available: http://www.ece.drexel.edu/walsh/waspaa07.pdf
