A mechanism for improved talc pleurodesis via foam delivery
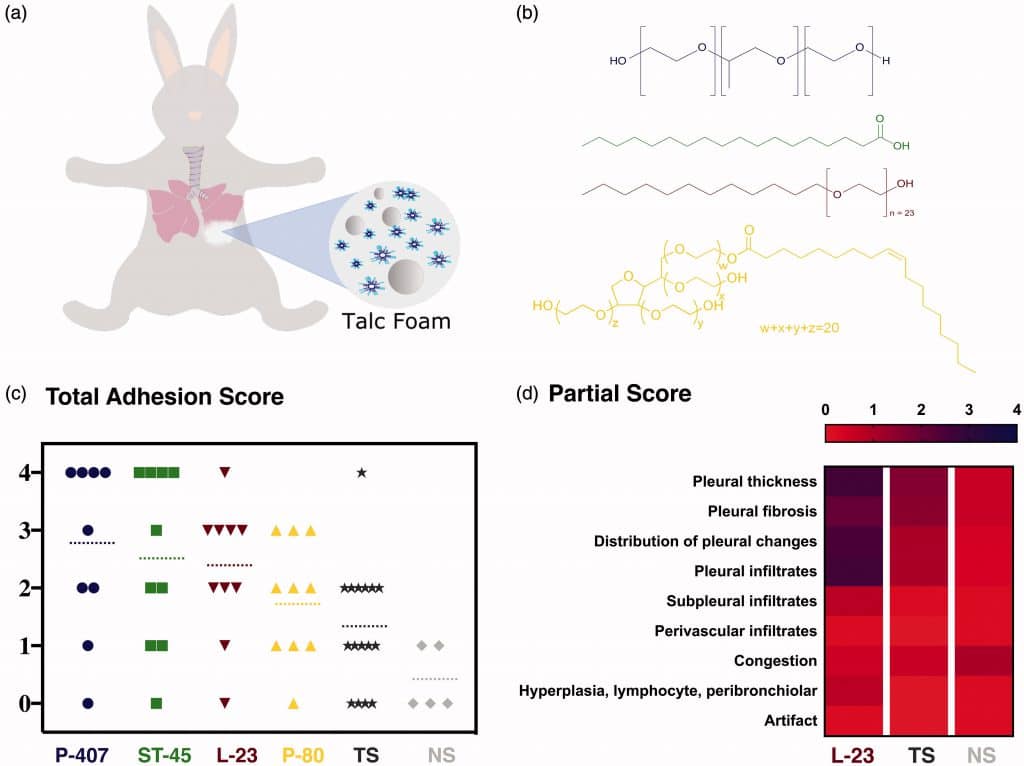
(a) Scheme of talc-foam pleurodesis in rabbit model. (b) Chemical structures of the surfactant present in each formulation: poloxamer (blue), stearic acid (green), laureth-23 (red) and polysorbate 80 (yellow). (c) Total adhesion score of each rabbit obtained from pleurodesis using the controls NS (light gray) and TS (dark gray), and the talc foams P407 (blue), ST-45 (green), L-23 (red) and P-80 (yellow).The dashed lines correspond to the average score over all rabbits tested for each formulation. (d) Heat map of partial scores achieved in rabbits treated with L-23, TS and NS.
Abstract
Talcum powder is recognized as the leading drug for pleurodesis, a treatment of choice for malignant pleural effusions. Recently, it was shown that hydrogel foam delivery systems significantly enhanced the number of adhesions between the chest wall and the lung in a New Zealand rabbit model due to the sol-gel transition. However, many questions still remain regarding the cause of improved efficacy, such as: (1) Would only hydrogel foams improve the efficacy of talc pleurodesis? (2) Is it possible to achieve the same efficacy of hydrogels using non-hydrogel foams? 3) What are the physicochemical properties that can be correlated to the efficacy of talc pleurodesis? In this study, we use non-hydrogel foam formulations to determine the efficacy of pleurodesis. Foam stability and rheology of the formulations were correlated to adhesion formation. The results clearly suggest a correlation of pleurodesis efficacy to the viscosity and modulus of the foam delivery system.
Publication Metadata
Authors
T. A. Lima, R. A. Coler, G. W. Laub, S. Sexton, L. Curtin, K. M. Laub & N. J. Alvarez
Keywords
Citation
T. A. Lima, R. A. Coler, G. W. Laub, S. Sexton, L. Curtin, K. M. Laub & N. J. Alvarez (2021) A mechanism for improved talc pleurodesis via foam delivery, Drug Delivery, 28:1, 733-740, DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1895910
Related Publications
We are still importing publications to our site. Please check back later.
