Laboratory Equipment
Material Synthesis and Characterization
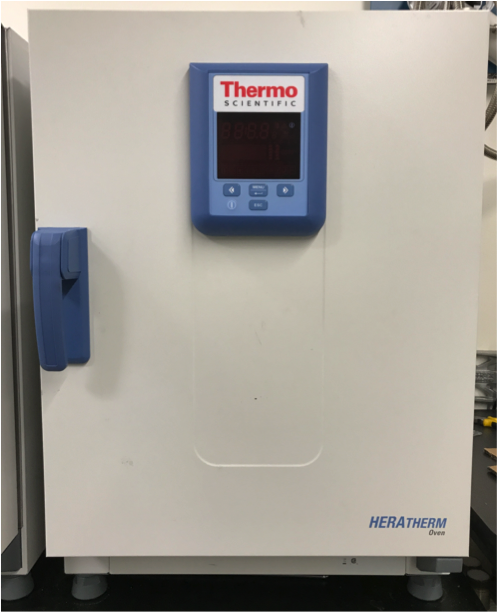

Lab Ovens
Used for drying samples, thermal treatments, and hydrothermal synthesis. Temperature range of 60-325° C.

Box Furnace
Furnace for annealing materials at temperatures of up to 1100°C.
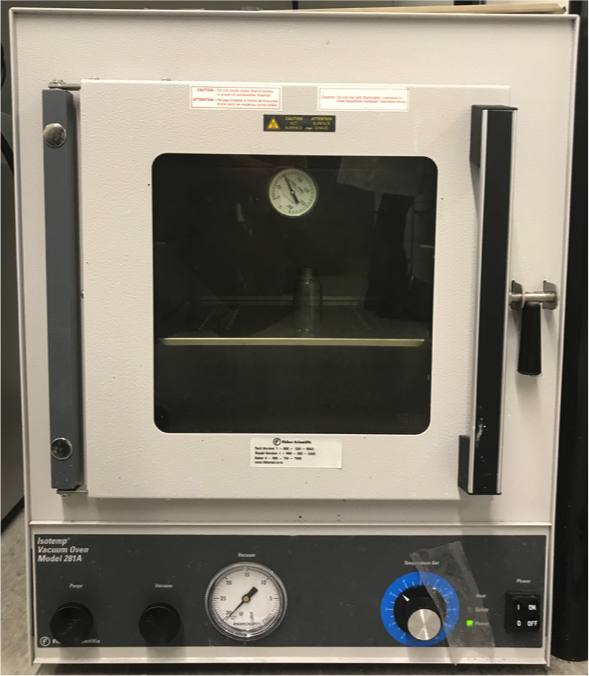

Vacuum Oven
Oven for drying and annealing samples under vacuum with a temperature range of 60-300° C.
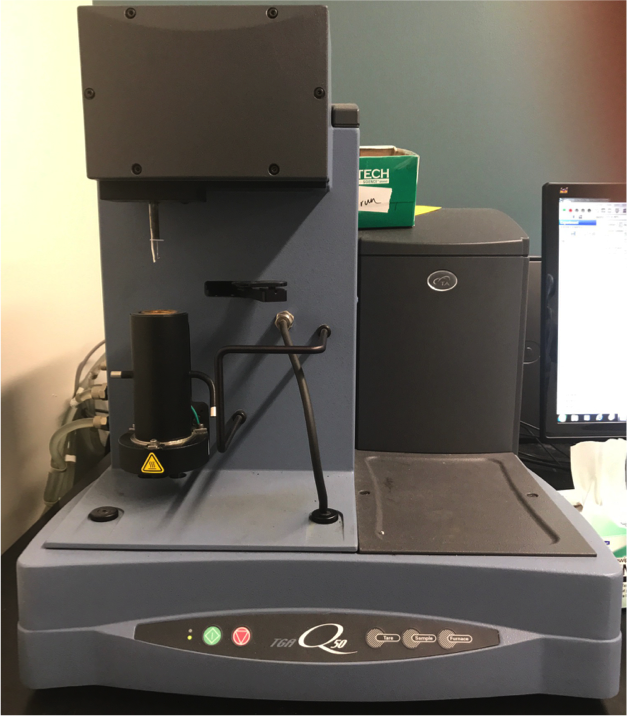

Thermogravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis instrument for measuring change in sample mass while sample is heated in either air or inert environment.
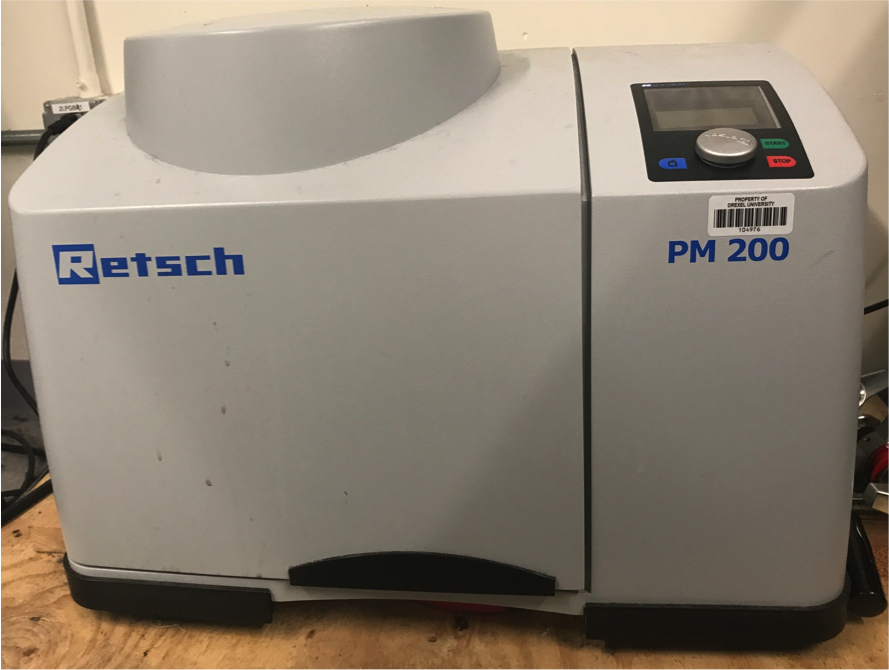

Planetary Mixer
High energy planetary mixer used to grind materials into uniform, small particles and homogenously mix materials.
Electrochemical Characterization
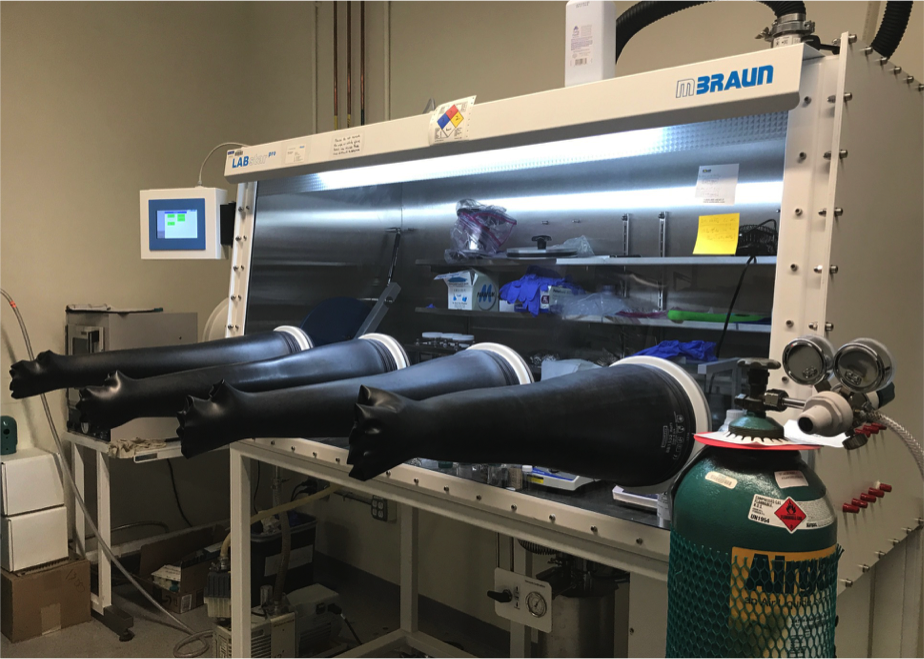

Glovebox
Argon-filled, inert glovebox used for electrolyte fabrication and coin cell assembly. As many electrolyte salts and counter electrode metals react highly with air and/or water, battery fabrication must be conducted in an inert environment.
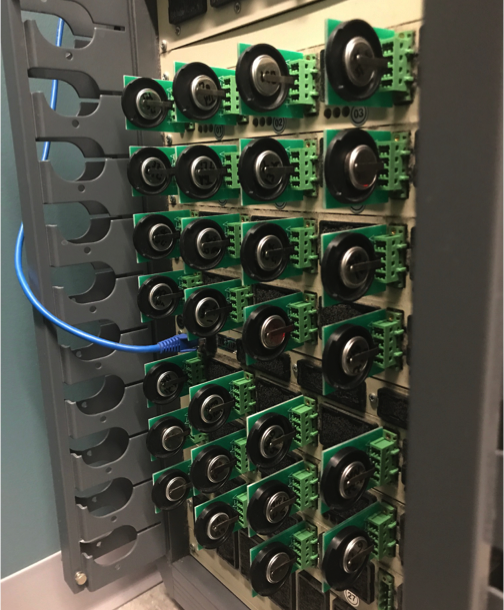

Arbin Battery Testing Station
Battery testing station capable of testing 28 coin cells or other electrochemical devices. Galvanostatic cycling, rate performance, and galvanostatic intermittent titration technique (GITT) tests are performed using this device.
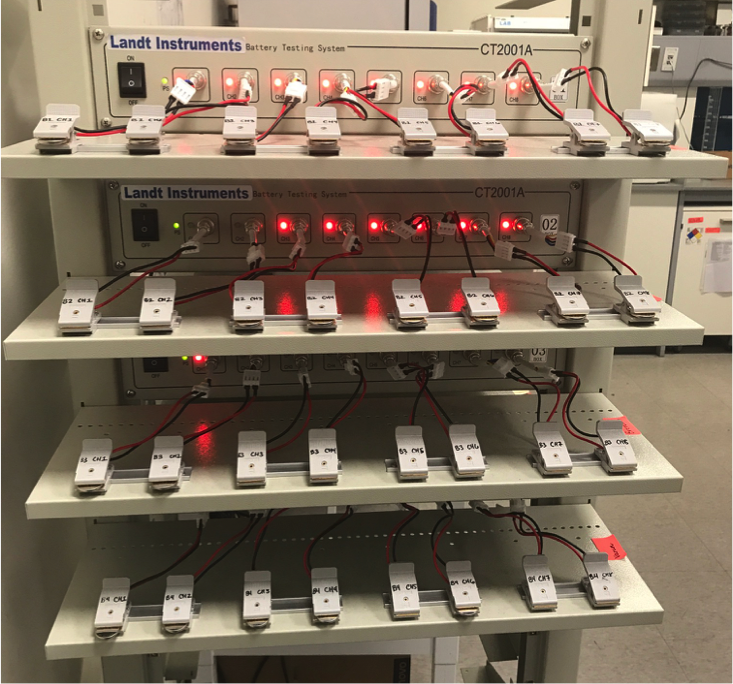

Landt Battery Testing Station
Battery testing station capable galvanostatic cycling of 32 coin cells or other electrochemical devices.
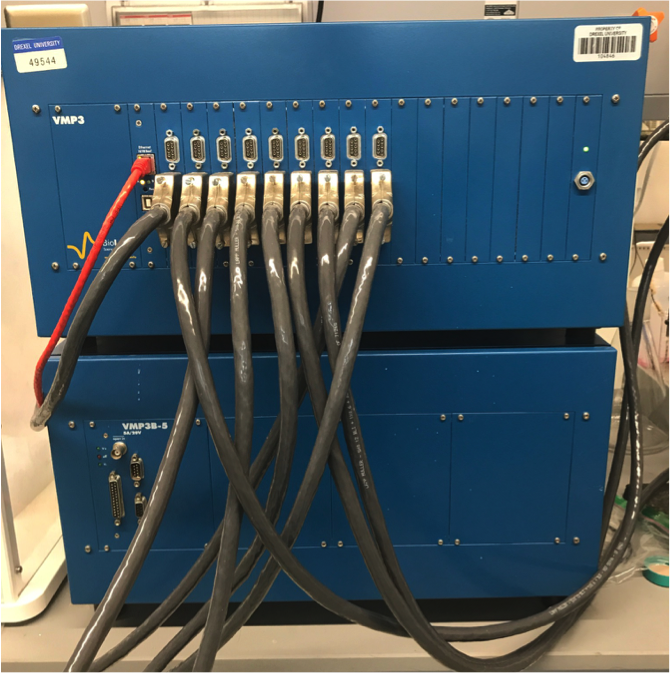

Biologic VMP3 Potentiostat
9 channel potentiostat with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) capabilities that is capable of testing all electrochemical cells fabricated in the lab under a wide variety of conditions.
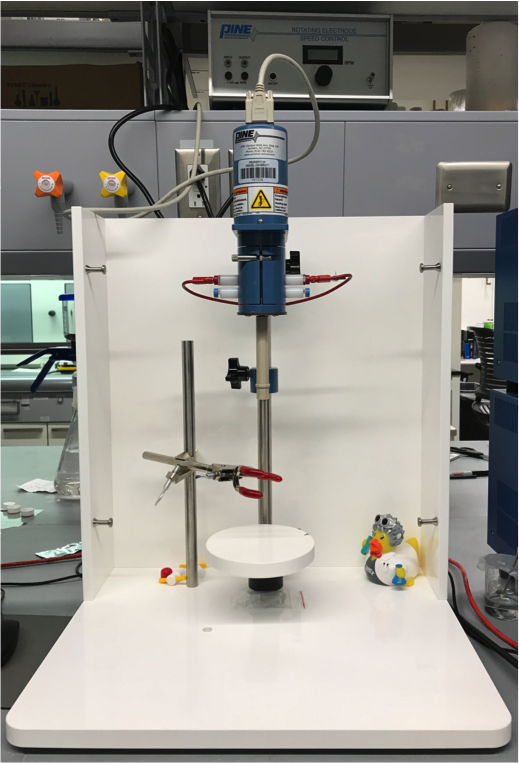
Pine Rotating Disk Electrode
Electrochemical testing station that allows for working electrode to be rotated at high speeds in electrolyte solution. Rotator is attached to Biologic Potentiostat so that electrochemical behavior of system being tested can be monitored.
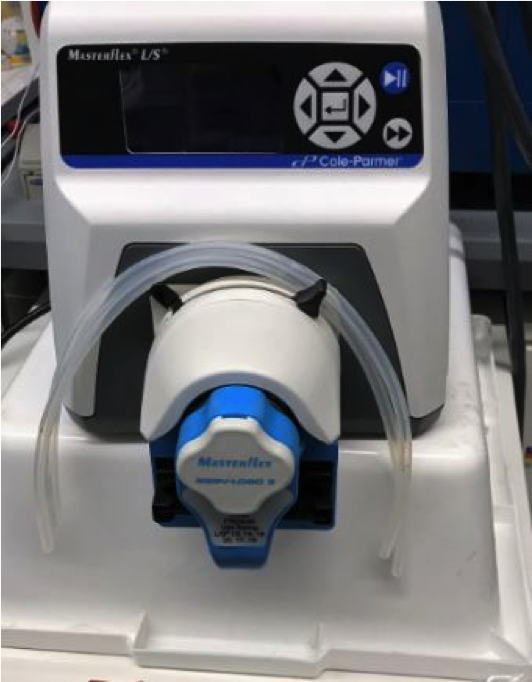

Cole Palmer Masterflex Pump
Pump with controllable flow rates used for testing materials in capacitive deionization cells. Second pump head enables two cells to be tested simultaneously.
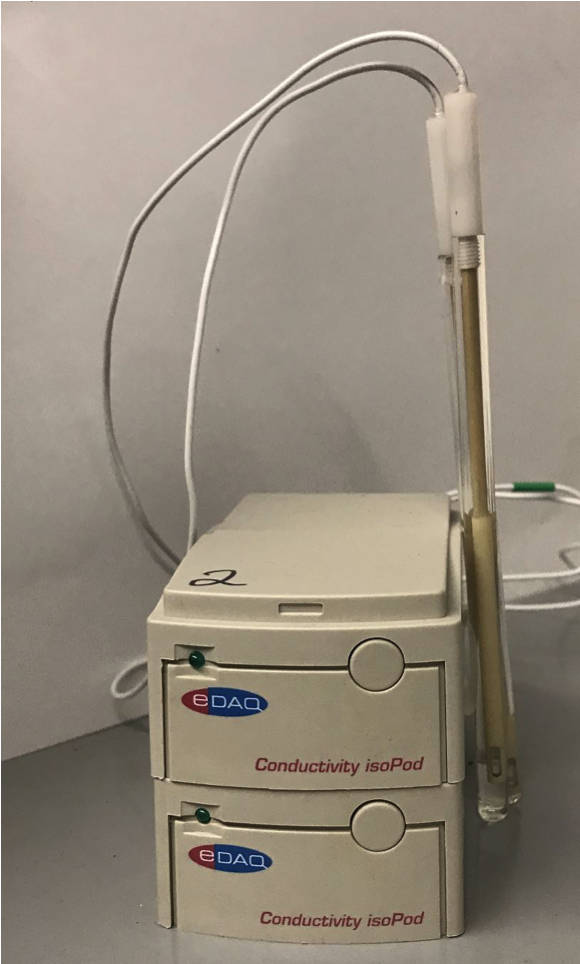

Conductivity Probe
Dip-in conductivity probes that continuously monitor conductivity of a solution. These probes have the ability to record conductivity measurements for days, allowing for important CDI metrics to be calculated from the data.
Electrodes Preparation

Filtration
Solutions containing active material are vacuum filtered through a polypropylene membrane to create a free-standing electrode film. This can be used with multiple different electrode materials or conductive additives to create hybrid or composite films.
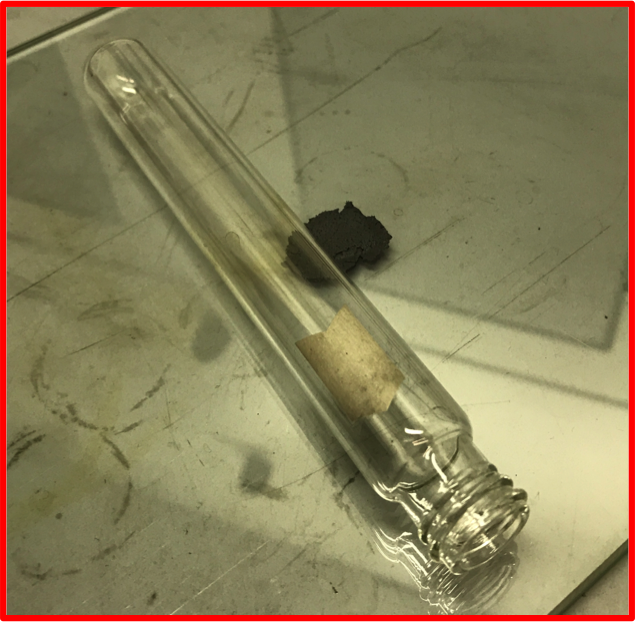

Film Rolling
Films consisting of active material, carbon black, and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are rolled out onto a glass slide to create a free-standing film. This method is commonly used to make electrode films for supercapacitor, pseudocapacitor, and hybrid capacitive deionization studies.
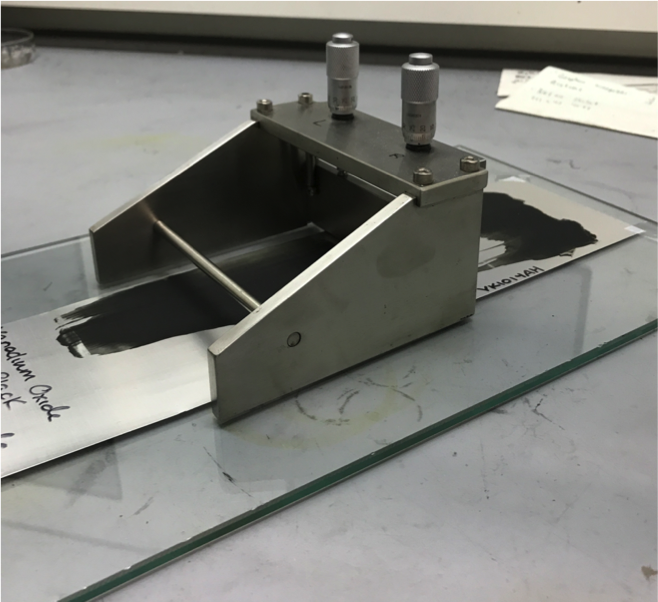
Film Casting
A commonly utilized method for creating battery electrode films. A doctor blade is used to draw out a slurry of active material, carbon black, and a polymer binder.
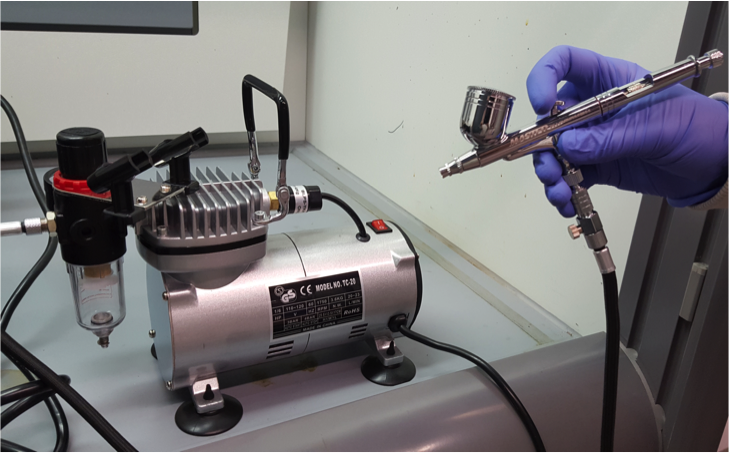

Spray Coating
Solutions containing active material are sprayed onto a substrate to create uniform, thin electrode films. This can be used with multiple different electrode materials or conductive additives to create hybrid or composite films.
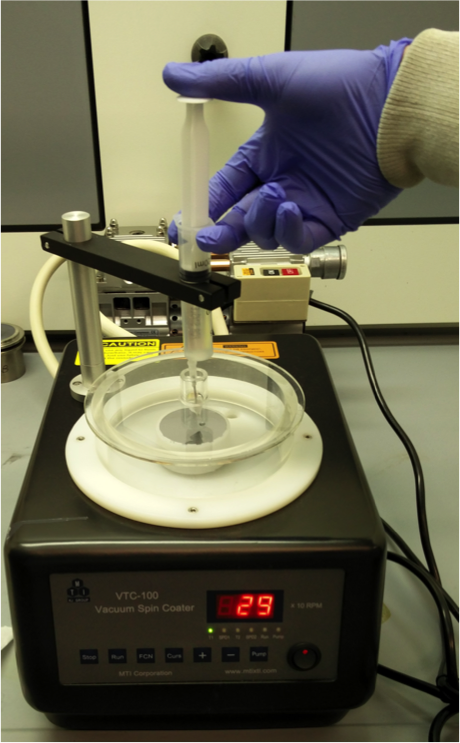
Spin Coating
Solutions containing active material are dropped onto a substrate that is spun at high speed to create an electrode film. This can be used with multiple different electrode materials or conductive additives to create hybrid or composite films.